Branch Discovery SDK
The Branch Discovery SDK is an Android SDK provided by Branch to power in-app search on Android devices. This SDK is a thin wrapper with helper classes to assist in building search user experiences on top of the Branch Discovery API. This SDK and API allow your users to search through the tens of billions of deep links to app pages that Branch has indexed from its core linking platform used by tens of thousands of mobile applications.
Getting Started
Installation
The compiled Branch Discovery SDK footprint is approximately 40kb
Install Branch Discovery SDK
Add implementation 'io.branch.sdk.android:search:1.x.y' to the dependencies section of your build.gradle file, where x and y correspond to the latest release version.
Additional dependencies and permissions
Permissions
- Internet access permissions are required in order to request and return search results as you would expect
- (optional, but strongly recommended) Location permission. When enabled, location will greatly enhance search results and is required in order to display local results. If your project does not already use location services, you will need to add the following to your
build.gradledependency list:
implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-location:' + PLAY_SERVICE_VERSION
- (mandatory) Google Play services to access advertising IDs. This lets Branch use its network of app usage information to personalize and improve the user experience. To support this, make sure the following is in your build.gradle dependency list:
implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-ads:' + PLAY_SERVICE_VERSION
- (mandatory) Add okhttp library to handle network requests
implementation 'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:3.12.6'
Register Your App
You will need to sign up here to request a a [Branch Discovery API Key] (https://branch.io/discovery-signup/).
Add your Branch key to your project.
Once you receive your Branch Discovery API Key, edit your app's manifest file to include the following:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="io.branch.sample"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
<application>
<!-- Other existing entries -->
<!-- Add this meta-data below, and change "key_live_xxxxxxx" to your actual live Branch key -->
<meta-data android:name="io.branch.sdk.BranchKey" android:value="key_live_xxxxxxx" />
</application>
</manifest>
Integrating Branch Discovery SDK
Initialization
The Branch Discovery SDK needs to be initialized before using any search functionality. The SDK can be initialized anywhere within your application. Ideally should be from the onCreate() method of the application class. Alternatively it can be initialized from the onCreate() method of the Activity, however subsequent calls to init() will not reinitialize the SDK.
BranchSearch.init(getApplicationContext());
Hints
To educate your users on the value of in-app search, this endpoint will return you a short list of query "hints" that you can suggest to the user to try, even before they've began to type a search query. These are trending queries from a range of content verticals.
BranchQueryHintRequest request = BranchQueryHintRequest.create();
BranchSearch.getInstance().queryHint(request, new IBranchQueryHintEvents() {
@Override
public void onBranchQueryHintResult(@NonNull BranchQueryHintResult result) {
Log.d("Branch", "QueryHint results: " + result.getHints().toString());
queryHints = result.getHints();
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
updateQueryHint();
}
});
}
@Override
public void onBranchQueryHintError(@NonNull BranchSearchError error) {
if (error.getErrorCode() == BranchSearchError.ERR_CODE.REQUEST_CANCELED) {
Log.d(TAG, "Branch QueryHint request was canceled.");
} else {
// Handle any errors here
Log.d(TAG, "Error for Branch QueryHint. " +
error.getErrorCode() + " " + error.getErrorMsg());
}
}
});
When hints are clicked
When a BranchQueryHint object is clicked by the user, you can create a search request by passing the hint to BranchSearchRequest.create(BranchQueryHint), or simply use branchQueryHint.toSearchRequest(). This gives better analytics to Branch and let us improving the service.
BranchQueryHint clickedHint = ...;
BranchSearchRequest request = clickedHint.toSearchRequest();
BranchSearch.getInstance().query(request, ...);
The triggered search request can also be created by passing a String, in which case you should make sure to call BranchSearchRequest.setQuerySource(BranchQuerySource.QUERY_HINT_RESULTS).
Auto Suggest
As a user is typing, Auto Suggest (sometimes referred to as autocomplete) will return a list of query completions that reflet our best predictions for what the user is searching for. We strongly recommend you add Auto Suggest to your UI since it is a critical element of a modern search experience that users now expect.
BranchAutoSuggestRequest request = BranchAutoSuggestRequest.create("pizza");
BranchSearch.getInstance().autoSuggest(request, new IBranchAutoSuggestEvents() {
@Override
public void onBranchAutoSuggestResult(@NonNull BranchAutoSuggestResult result) {
Log.d("Branch", "onAutoSuggest: " + result.getSuggestions().toString());
}
@Override
public void onBranchAutoSuggestError(@NonNull BranchSearchError error) {
if (error.getErrorCode() == BranchSearchError.ERR_CODE.REQUEST_CANCELED) {
Log.d(TAG, "Branch AutoSuggest request was canceled.");
} else {
// Handle any errors here
Log.d(TAG, "Error for Branch AutoSuggest. " +
error.getErrorCode() + " " + error.getErrorMsg());
}
}
});
When suggestions are clicked
When a BranchAutoSuggestion object is clicked by the user, you can create a search request by passing the hint to BranchSearchRequest.create(BranchAutoSuggestion), or simply use branchAutoSuggestion.toSearchRequest(). This gives better analytics to Branch and let us improving the service.
BranchAutoSuggestion clickedSuggestion = ...;
BranchSearchRequest request = clickedSuggestion.toSearchRequest();
BranchSearch.getInstance().query(request, ...);
The triggered search request can also be created by passing a String, in which case you should make sure to call BranchSearchRequest.setQuerySource(BranchQuerySource.AUTOSUGGEST_RESULTS).
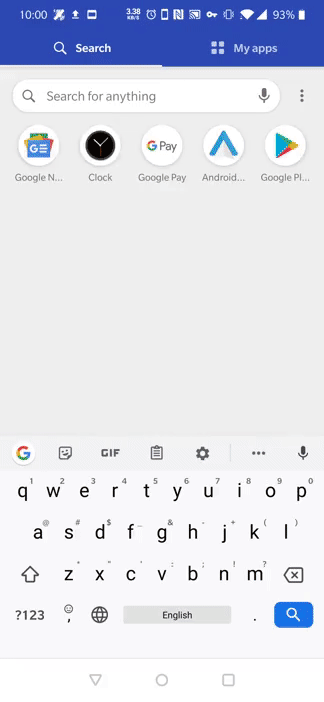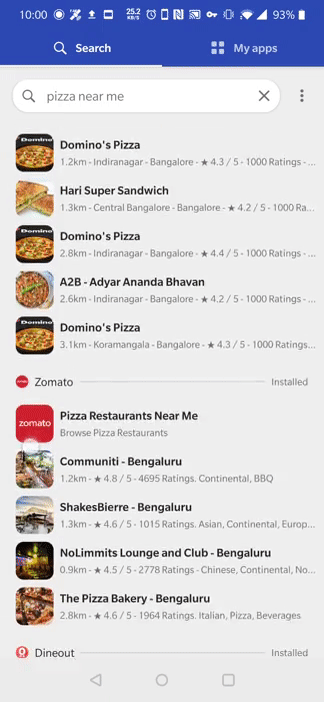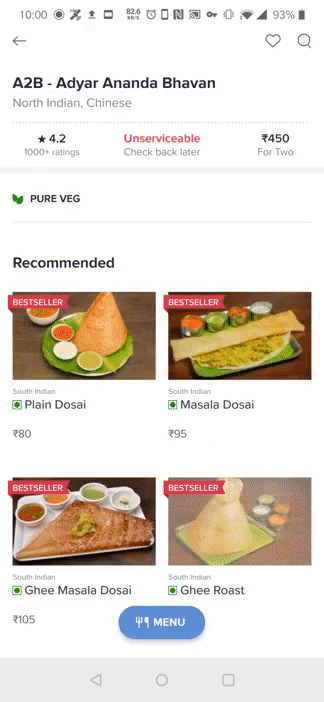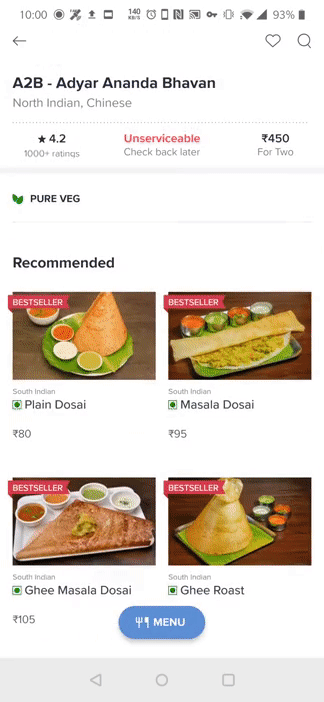
Search for In-App Content
When a user begins typing into your search box, you should create a BranchSearchRequest to search for apps and content with Branch. Create a builder for each phrase you would like to search for. Don't worry, we handle debounce so feel free to create one with every character entered.
Note that the Branch Discovery SDK will provide better results if it can use the current location. For example, a user searching for a restaurant will receive location specific results if location permissions are enabled. Be sure to pass the user location to BranchSearch.getInstance().setLocation()! For your reference, in io.branch.search.demo.util.BranchLocationFinder, we have provided example code that fetches the device's last known location.
// Create a Branch Search Request for the keyword
// Implementation Note: Set the last known location before searching.
BranchSearchRequest request = BranchSearchRequest.create(keyword);
// Search for the keyword with the Branch Search SDK
BranchSearch.getInstance().query(request, new IBranchSearchEvents() {
@Override
public void onBranchSearchResult(@NonNull BranchSearchResult branchSearchResult) {
// Update UI with search results. BranchSearchResult contains the result of any search.
branchSearchController.onBranchSearchResult(branchSearchResult);
}
@Override
public void onBranchSearchError(@NonNull BranchSearchError error) {
// Handle any search errors here
}
});
Controlling numbers of results
BranchSearchRequest is a builder and allows other attributes to be added to the query, such as limiting number of results per app or maximum number of results. Search results are always updated through the onBranchSearchResult(BranchSearchResult branchSearchResult) callback.
Maximum app results
You can control the maximum number of distinct app groups (see format of results in next section) that are returned by the API using the following code. The default is 5.
BranchSearchRequest.create(search_phrase)
.setMaxAppResults(10)
Maximum content per app
You can control the maximum number of content links that are returned per app (see format of results in next section) that are returned by the API using the following code. The default is 5.
BranchSearchRequest.create(search_phrase)
.setMaxContentPerAppResults(10)
Displaying the search results from BranchSearchRequest
The structure of the results in the query are as follows, and are intended to fit the expected presentation of results. The model is very similar to how Spotlight search results are structured: clustered by app, with a sub list of containing deep links. Here's a model that may be helpful:
`BranchSearchResult`
[
`BranchAppResult`
[
`BranchLinkResult`,
`BranchLinkResult`,
`BranchLinkResult`,
...
],
`BranchAppResult`
[
`BranchLinkResult`,
`BranchLinkResult`,
`BranchLinkResult`,
...
],
...
]
BranchSearchResult Class
The BranchSearchResult object is returned to you from a successful query and contains some information relevant for processing search results. The object has the following important properties:
| Method | Return Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| getBranchSearchRequest | BranchSearchRequest |
The original search request of format BranchSearchRequest that triggered this specific set of results. Note that you can reference the original query by calling getQuery() on this object. |
| getCorrectedQuery | String | If this field is non-null, it will represent the spell-corrected query that was actually used to search. Recommend that you show feedback to user such as "Showing results for + " |
| getResults | List<BranchAppResult> |
A list of BranchAppResult objects representing the application results matched for the search request. Attached to each object is also the deep link list to show in this group. |
BranchAppResult class
Branch will return to you a list of relevants apps for each query, similar to if the user were searching on-device or via the Play Store. The app results are returned in the appResults list in the BranchSearchResult object. A few key parameters of this object are:
| Method | Return Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| getAppName | String | Gets the name of the app for display |
| getPackageName | String | Gets the package name of the app |
| getAppIconUrl | String | Gets the URL of the app icon for display |
| getDeepLinks | List | Gets the list of BranchLinkResult objects for display |
| openSearchDeepLink(Context, Boolean fallbackToPlayStore) | BranchSearchError | The method to trigger when a user clicks on the header. This will attempt to trigger the search deep link to continue the user query in the app. Some apps dox not support this, and the fallback will trigger openApp. |
| isSearchDeepLinkAvailable() | boolean | This method will return true if the search deep link is available. This can be used to change the UI based on its presence. |
| openApp(Context, boolean fallbackToPlayStore) | BranchSearchError | If you just want to open the app without searching, use this method. Specify as argument whether you want the user to go to the Play Store when app is not installed |
BranchLinkResult class
Branch will also return relevant content to the user query. These are deep links to pages inside of apps, ranked in a personal way for the user. Note that we will also return content for apps that are not installed. In the case that the app is not installed, we will route the user to the web page version of the content if available. Not all applications have websites though.
| Method | Return Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| getName | String | Gets the title of the content for display |
| getDescription | String | Gets the description of the content for display |
| getImageUrl | String | Gets the URL of the content image for display |
| isAd | boolean | Is this link an advertisement -- e.g. a sponsored result |
| openContent(Context, boolean fallbackToPlayStore) | BranchSearchError | Branch is great at deep link routing, so we wanted to abstract away this complexity from you. When a user taps on an action, you simply need to call completeAction() to trigger the user to be routed to the content or website. |
| openDeepView(FragmentManager) | BranchSearchError | Opens the link into a Branch Deepview. The content preview will be rendered inside a in-app web view with the option to download the app from the play store. |
| registerClickEvent() | none | If you decide to handle routing on your own with the URI scheme / web link included in the link result, please call this method when the user taps. This is not required if you use openContent or openDeepView |
Handling errors with BranchSearchError
The only thing consistent when working in mobile is that the network can fail regularly. Plus, there are all sorts of other reasons your search request might fail. Inevitably, you'll need to handle the variety of reasons why the request might fail, and we started to accumulate some of the common ones we see.
BranchSearchError class
Here are the possible methods to use on the error object:
| Method | Return Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| getErrorCode | enum ERR_CODE | One of a variety of error codes that may happen, listed below |
| getErrorMsg | String | Gives you a nice readable reason for known errors and a generic one for unknown errors |
And here are the actual codes and corresponding root causes:
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
| UNKNOWN_ERR | An unknown error occurred. |
| BAD_REQUEST_ERR | This means your request was missing a some important parameter. |
| UNAUTHORIZED_ERR | This means that your Branch key is not white listed to use the API. Please let us know to address. |
| NOT_SUPPORTED_ERROR | This is likely because you're trying to use the search API in a region that Branch doesn't currently support. |
| NO_INTERNET_PERMISSION_ERR | Poor network connectivity. Please try again later. Please make sure app has internet access permission. |
| BRANCH_NO_CONNECTIVITY_ERR | Please add 'android.permission.INTERNET' in your applications manifest file. |
| INTERNAL_SERVER_ERR | Unable to process your request now. An internal error happened. Please try later. |
| REQUEST_TIMED_OUT_ERR | Request to Branch server timed out. Please check your connection or try again later. |
| ROUTING_ERR_UNABLE_TO_OPEN_APP | Unable to open the destination application or its fallback url. |
| ROUTING_ERR_UNABLE_TO_OPEN_WEB_URL | Unable to open the web url associated with the app. |
| ROUTING_ERR_UNABLE_TO_OPEN_PS | Unable to open the Google Play Store for the app. |
| ROUTING_ERR_UNABLE_TO_COMPLETE_ACTION | An unknown error happened. Unable to open the app. |
Special Shortcut Handling (for non-Launchers)
This section only applies to Android clients that are not Launchers
Some shortcut links returned by Branch can only be opened by a launcher. To open such links, the Branch Discovery SDK utilizes a permission for interacting with the LauncherApps Service that Android grants the default launcher. If the SDK determines that it does not have this permission, it will not include these shortcut links in the search results. If your client has alternate access to the LauncherApps Service, you may override how the SDK handles these shortcut links.
IBranchShortcutHandler Interface
Branch provides an easy way to override how the SDK accesses the LauncherApps Service via the io.branch.search.IBranchShortcutHandler interface. You can create a class that implements this interface and set your class as the shortcut handler via setShortcutHandler method in your BranchConfiguration. The IBranchShortcutHandler interface has 2 methods you will implement:
| Method | Return Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| validateShortcut | boolean | Validates whether shortcut with given id and package name is valid. Should return true if the specified shortcut is active. |
| launchShortcut | boolean | Attempts to launch shortcut with given id and package name. Should return true if shortcut is successfully launched. |